Why Data Recovery Matters
In today’s digital world, data is one of the most valuable assets we own, whether it’s personal memories, financial records, business files, or sensitive research. Losing access to this information can have consequences that range from mild inconvenience to severe financial or professional damage.
For individuals, losing family photos, personal projects, or important documents can be devastating, as these items are often irreplaceable. For businesses, data loss may result in operational downtime, regulatory fines, or loss of customer trust. In some industries, even a few hours of downtime can cost thousands of dollars.
Another reason why recovery matters is that data loss can occur suddenly and unpredictably. A hard drive may fail without warning, malware can encrypt entire systems, or a simple human error like formatting the wrong disk can wipe years of work in seconds. Because of this unpredictability, knowing how to act quickly and efficiently when data loss strikes is crucial.
Beyond the immediate consequences, there are also long-term implications. For example, organizations that fail to recover or protect their data risk legal liabilities and compliance violations, especially when dealing with sensitive information such as medical records or financial data. Even at a personal level, losing access to critical files may hinder education, career opportunities, or creative projects.
Ultimately, data recovery matters because it ensures that when accidents, failures, or attacks happen, you still have a path to restore what is lost. Having the knowledge and resources to attempt recovery—or knowing when to seek expert help—can make the difference between temporary disruption and permanent loss.
Understanding Data Loss Scenarios
Before deciding how to recover data, it’s essential to understand the different scenarios that can lead to data loss. Each situation carries its own risks and may require a unique recovery approach. Identifying the cause helps determine whether a do-it-yourself method might work or if expert intervention is necessary.
1. Accidental deletion: One of the most common scenarios, this happens when files are mistakenly removed from a system. While modern operating systems often provide a recycle bin or trash folder, permanent deletion can still occur if these temporary storage areas are emptied. In such cases, recovery is possible if the deleted data hasn’t been overwritten by new files.
2. File system corruption: When the structure that organizes and manages files becomes damaged, data may appear missing or inaccessible. Causes include improper shutdowns, software bugs, or power failures. Although the files themselves might still exist, the operating system cannot read them without specialized tools.
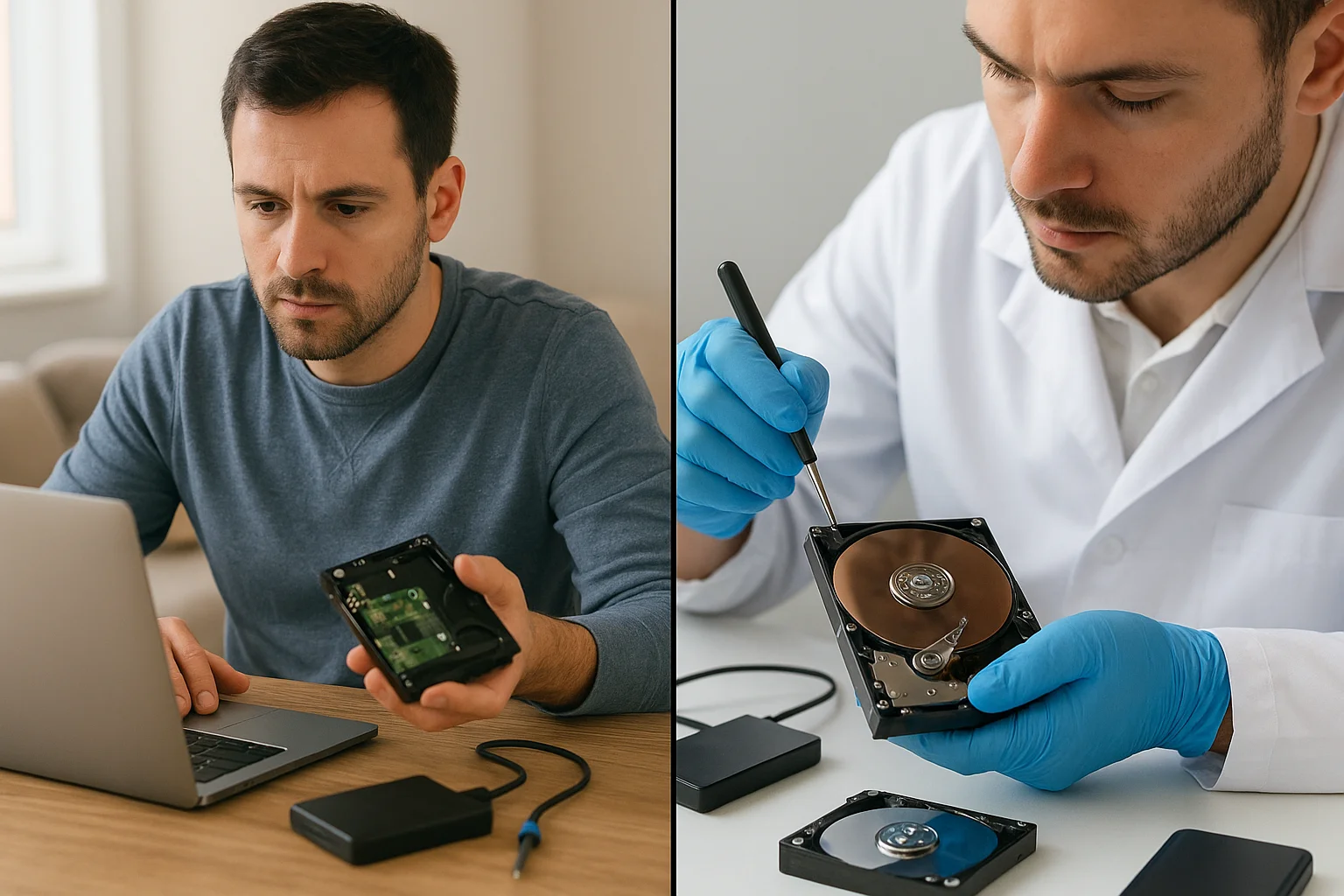
3. Hardware failure: Hard drives, SSDs, and external storage devices are prone to mechanical or electronic malfunctions. Clicking sounds, unusual heat, or complete device failure often point to physical damage. These cases are typically more complex and often demand professional recovery techniques.
4. Malware and ransomware attacks: Malicious software can encrypt, hide, or delete files. Ransomware, in particular, locks users out of their data until a payment is made. Even after removal of the malware, recovery can be extremely difficult without secure backups or advanced decryption methods.
5. Formatting or partition errors: Reformatting a drive or altering partitions by mistake can erase large amounts of data instantly. While the data might not be completely gone, recovering it requires tools capable of scanning the drive for lost structures and file fragments.
6. Natural disasters and environmental factors: Floods, fires, and extreme temperatures can destroy storage media. In such events, physical recovery is highly challenging and may require specialized cleanroom environments to even attempt restoration.
7. Human error beyond deletion: Mismanaging devices, unplugging drives during transfers, or improper handling of external storage can all lead to corruption or loss. These errors may not always be obvious at first, but the damage they cause can accumulate over time.
By recognizing the variety of scenarios that cause data loss, users can better evaluate the seriousness of their situation and decide on the most appropriate recovery strategy.
DIY Data Recovery: When It’s Safe to Try
Not every case of data loss requires expensive equipment or expert assistance. In some situations, attempting DIY data recovery can be both safe and effective, provided the issue is not related to severe hardware damage. The key is knowing when it’s reasonable to try and when the risks outweigh the potential benefits.
1. Recently deleted files: If files were deleted accidentally but the storage device is still functioning normally, DIY tools can often restore them. Until recovery is attempted, it’s important to avoid saving new files to the same drive, as this increases the risk of overwriting the lost data.
2. Logical errors without physical damage: When a file system becomes corrupted due to a software error or improper shutdown, recovery software may be able to scan the drive and rebuild missing directory structures. These scenarios are generally low-risk for users to attempt on their own.
3. External drives or removable media: USB sticks, SD cards, and external hard drives often suffer from accidental formatting or simple corruption. Because these devices can be disconnected and cloned easily, they are relatively safe candidates for DIY recovery attempts.
4. Using specialized software: There are many tools designed for end-users that can perform tasks such as scanning for deleted files, reconstructing partitions, or recovering from accidental formatting. Programs like these usually provide a read-only mode, which ensures that the software does not modify the original drive during the recovery process. This adds an extra layer of safety.
5. Data from secondary drives: Attempting recovery on a drive that is not running the operating system is generally safer. Boot drives are more sensitive since the system writes data to them constantly. Recovering from a secondary or external drive minimizes the chance of overwriting critical files.
Precautions before starting: Before trying DIY recovery, it is advisable to create a full disk image of the affected drive. This allows recovery attempts to be made on the copy, protecting the original from further damage. Additionally, users should ensure the power supply is stable and avoid using the affected drive until recovery is complete.
DIY data recovery is a valuable option for advanced users who understand the risks and limits. In the right circumstances, it provides a cost-effective way to retrieve important files without needing professional services.
The Risks of DIY Recovery
While attempting to restore lost data on your own can be appealing, there are significant risks associated with DIY recovery. In many cases, well-intentioned actions can worsen the situation, reducing the chances of successful retrieval or even making recovery impossible.
1. Overwriting data: One of the most common mistakes is continuing to use the affected device while trying to recover files. Every new file written to the drive may overwrite parts of the deleted or corrupted data, making it permanently inaccessible. Even system processes running in the background can unintentionally overwrite critical sectors.
2. Using unreliable or unsafe software: Not all recovery tools are created equal. Some free or poorly designed programs may introduce malware, additional corruption, or unwanted changes to the drive. Others might lack read-only modes, meaning they attempt recovery by directly altering the disk, which increases the risk of permanent loss.
3. Misdiagnosing the problem: A drive that appears to have logical corruption could actually be suffering from underlying hardware issues. Running recovery software on a failing hard drive can cause it to deteriorate further, as the process often requires intensive reading and scanning. What might have been recoverable in a controlled environment can become irretrievably damaged.
4. Physical damage risks: Opening a hard drive outside of a specialized cleanroom environment can allow dust and contaminants to reach the platters, scratching the delicate surfaces and destroying data. Similarly, using home repair attempts like freezing a drive or tapping it to “unstick” components can cause irreversible harm.
5. Partial or corrupted recovery: Even if DIY methods manage to retrieve some files, there’s a chance that they may be incomplete, corrupted, or unusable. Without specialized tools to rebuild fragmented or encrypted data, the results can be misleading, giving the impression that recovery was successful when the files are actually compromised.
6. Voiding warranties or support options: Some manufacturers or professional services may refuse to work on devices that have been tampered with using unsafe recovery attempts. This means that experimenting with DIY fixes might remove the possibility of future professional intervention.
7. Time and resource costs: Recovery processes can be time-consuming, and unsuccessful attempts may lead to frustration while delaying a proper solution. In critical cases where data is highly valuable, this lost time can increase financial or operational damage.
For these reasons, users need to carefully weigh the risks before attempting any self-directed recovery. What seems like a cost-saving solution may ultimately reduce the likelihood of retrieving important information.
When to Call a Professional
There are situations where attempting recovery on your own can cause more harm than good. In these cases, seeking help from a professional data recovery service is often the safest and most effective option. Professionals have access to specialized tools, cleanroom facilities, and expertise that go far beyond what typical software or consumer methods can provide.
1. Signs of physical damage: If a hard drive emits unusual noises such as clicking, grinding, or buzzing, this is a strong indicator of mechanical failure. Continuing to power on the device or run software scans in this state can cause further damage. Only trained experts in controlled environments should handle physically failing drives.
2. Non-detectable or unresponsive drives: When a computer or external device does not recognize a storage medium at all, the issue may be electrical or mechanical. DIY methods typically cannot resolve these failures, as they require replacement of internal components or advanced diagnostic tools.
3. RAID, NAS, and complex storage systems: Advanced configurations such as RAID arrays or network-attached storage can fail in unpredictable ways. Rebuilding these systems without deep knowledge can easily result in permanent data loss. Professionals are trained to reconstruct arrays and retrieve data safely.
4. Critical or sensitive data: If the files in question include business records, legal documents, client data, or personal information of high value, the risks of DIY recovery may be unacceptable. Professional recovery ensures the highest chance of success while maintaining confidentiality and compliance with data protection standards.
5. Severe corruption or malware damage: When ransomware or advanced malware encrypts files, professional intervention may be the only way to attempt recovery. Experts may have access to proprietary decryption tools, forensic methods, or secure backups that end-users cannot obtain.
6. Evidence preservation: In situations involving legal disputes, fraud investigations, or cybersecurity breaches, tampering with storage devices can destroy valuable evidence. Data recovery specialists often work in coordination with forensic teams to ensure that information is recovered while preserving its integrity for legal use.
7. Failed DIY attempts: If recovery efforts at home have already been attempted without success, it’s best to stop immediately and consult professionals. Repeated failed attempts can reduce the chances of eventual success, as every new action risks altering or overwriting critical sectors.
Calling a professional at the right time not only protects the integrity of your files but also increases the likelihood of a complete and usable recovery. Acting early can prevent irreversible damage and ensure the best possible outcome.