Why Testing Backup Devices is Crucial
Backup devices play a fundamental role in any data protection strategy, but relying on them blindly can lead to disastrous consequences. Without regular testing, you risk discovering failures only when you need your backups the most — during a data loss event. This can result in irretrievable data, extended downtime, and costly recovery efforts.
One key reason to test backup devices is to detect hardware degradation. Over time, storage media such as hard drives, SSDs, tapes, or flash drives can develop bad sectors, wear out, or suffer physical damage that reduces their reliability. Testing helps identify these problems early, allowing you to replace or repair devices before they fail.
Additionally, testing uncovers data corruption or incomplete backups. Even if a device powers on and appears functional, the backed-up data may be corrupted due to write errors, interrupted processes, or software glitches. Without verification, corrupted backups provide a false sense of security.
Regular testing also ensures that your backup and restore procedures work as expected. It’s one thing to back up data; it’s another to successfully restore it in a timely manner. Testing simulates real recovery scenarios, confirming that backups are not only complete but also accessible and usable.
Finally, backup device testing supports compliance with industry regulations and organizational policies. Many standards require proof of backup integrity and recoverability, which can only be demonstrated through documented testing. Neglecting this step can expose you to legal and financial penalties.
Understanding Different Types of Backup Devices
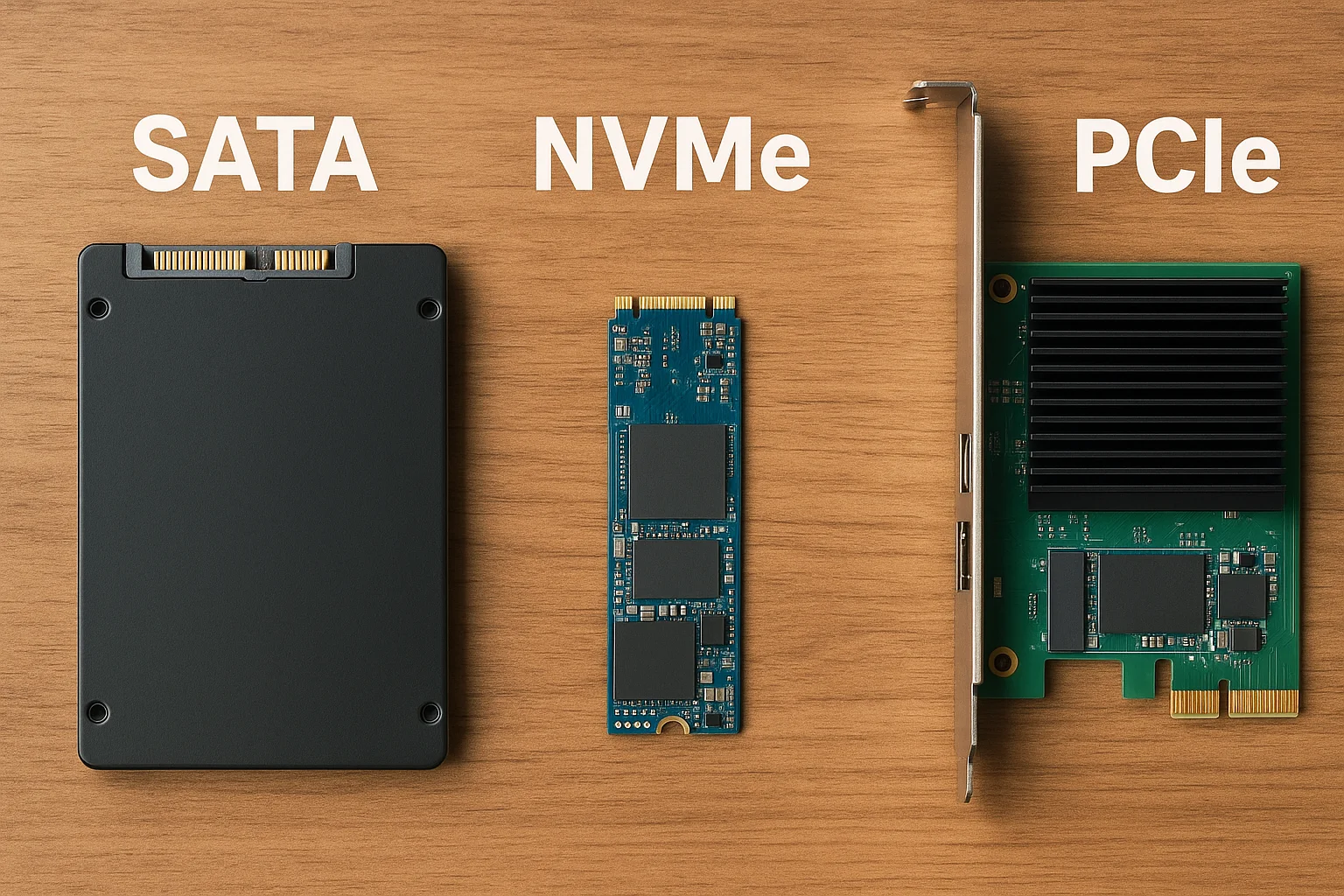
To effectively test the reliability of your backup system, it's important to understand the various types of backup devices available, as each comes with its own strengths, weaknesses, and testing requirements.
External Hard Drives (HDDs and SSDs) are among the most common backup devices. HDDs offer large storage capacity at a lower cost but are more susceptible to mechanical failure due to moving parts. SSDs, on the other hand, provide faster speeds and better durability because they have no moving components, but they usually come at a higher price and have a limited number of write cycles. Testing these devices often involves checking for physical wear, read/write errors, and ensuring data integrity.
Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices connect to your network, allowing multiple users to back up and access data centrally. NAS devices often include RAID configurations to improve fault tolerance. However, RAID is not a substitute for backups; it protects only against hardware failure. Testing NAS units involves verifying RAID health, network connectivity, and backup process reliability.
Magnetic Tape Drives have been a traditional choice for long-term backup storage due to their cost-effectiveness and longevity. Though slower in data transfer, tapes are well-suited for archival purposes. Testing tapes requires verifying readability over time, ensuring tape drives are calibrated correctly, and confirming that backup software interacts properly with the tape system.
Cloud Backup Services have gained popularity due to their offsite storage benefits and scalability. While the physical hardware is managed by the provider, it remains critical to test your ability to restore data from the cloud efficiently. This includes validating bandwidth performance, backup completeness, and access permissions.
USB Flash Drives are portable and convenient for quick backups but are generally not recommended for critical or large-scale backups due to limited durability and storage capacity. Testing USB drives focuses on detecting file corruption and verifying consistent read/write performance.
Understanding these devices’ unique characteristics allows you to tailor your testing methods effectively, ensuring that each backup medium performs reliably in protecting your data.
Performing Regular Backup and Restore Drills
One of the most effective ways to ensure the reliability of your backup devices is to perform regular backup and restore drills. These drills simulate real-world scenarios where data loss occurs and you need to recover quickly, helping you verify both the integrity of your backups and the efficiency of your restoration process.
Start by scheduling these drills at consistent intervals—monthly, quarterly, or according to your organization's risk tolerance and compliance requirements. The goal is to practice recovering different types of data from various backup devices to cover all bases.
During a drill, initiate a full or partial restore of data from the backup device to a separate test environment or secondary system. This approach avoids disrupting live systems while allowing you to confirm that:
- Backups are complete and uncorrupted.
- The restoration process functions without errors or delays.
- Files and applications behave as expected after restoration.
It’s essential to document every step of the drill, including the time taken to complete restores and any issues encountered. This documentation helps identify bottlenecks or technical problems that need addressing.
In addition to full restores, consider testing incremental and differential backups if your backup strategy uses these methods. Each type has different restoration procedures and potential points of failure that need validation.
Beyond technical verification, restore drills also serve to train your IT staff or anyone responsible for data recovery. Familiarity with the restoration process ensures that when a real incident occurs, the team can act swiftly and confidently.
Lastly, incorporate unexpected scenarios in your drills, such as restoring from offsite locations or recovering data after simulated hardware failure, to ensure your backup strategy is resilient under diverse conditions.
Testing Backup Speed and Performance
Backup speed and overall performance are critical factors that impact how quickly and efficiently you can secure and restore your data. Slow backups can lead to incomplete processes, increased system downtime, and can strain network resources—making performance testing an essential part of your backup reliability checks.
Begin by measuring the write speed of your backup device during data transfers. This can be done using benchmarking tools or built-in diagnostics provided by your backup software. Consistently low write speeds might indicate hardware issues, fragmented storage, or network bottlenecks if you're using network-attached devices.
Similarly, evaluate the read speed by performing test restores or reading large amounts of data from the backup device. This simulates the actual recovery process and reveals any potential slowdowns that could affect disaster recovery timelines.
For network-based backups, it’s important to monitor the network throughput and latency during backup windows. Overloaded or unstable networks can drastically reduce backup speed, causing delays or failures. Use network monitoring tools to identify congestion and optimize traffic flow.
Another factor to consider is the backup window—the scheduled time frame during which backups run. Testing performance allows you to verify that backups complete within this window without impacting other critical business operations.
Don’t overlook the impact of encryption and compression on backup performance. While these features enhance security and reduce storage space, they also require additional processing power. Performance tests should measure how these processes affect backup times and whether your hardware can handle the workload efficiently.
Finally, conduct tests under varying load conditions, such as backing up large files, numerous small files, or mixed data types. Different data profiles can influence backup speed, so understanding these nuances helps in optimizing your backup strategy.